Click on section name for complete set of plots
(900Hz - 2.5Sv Transport)
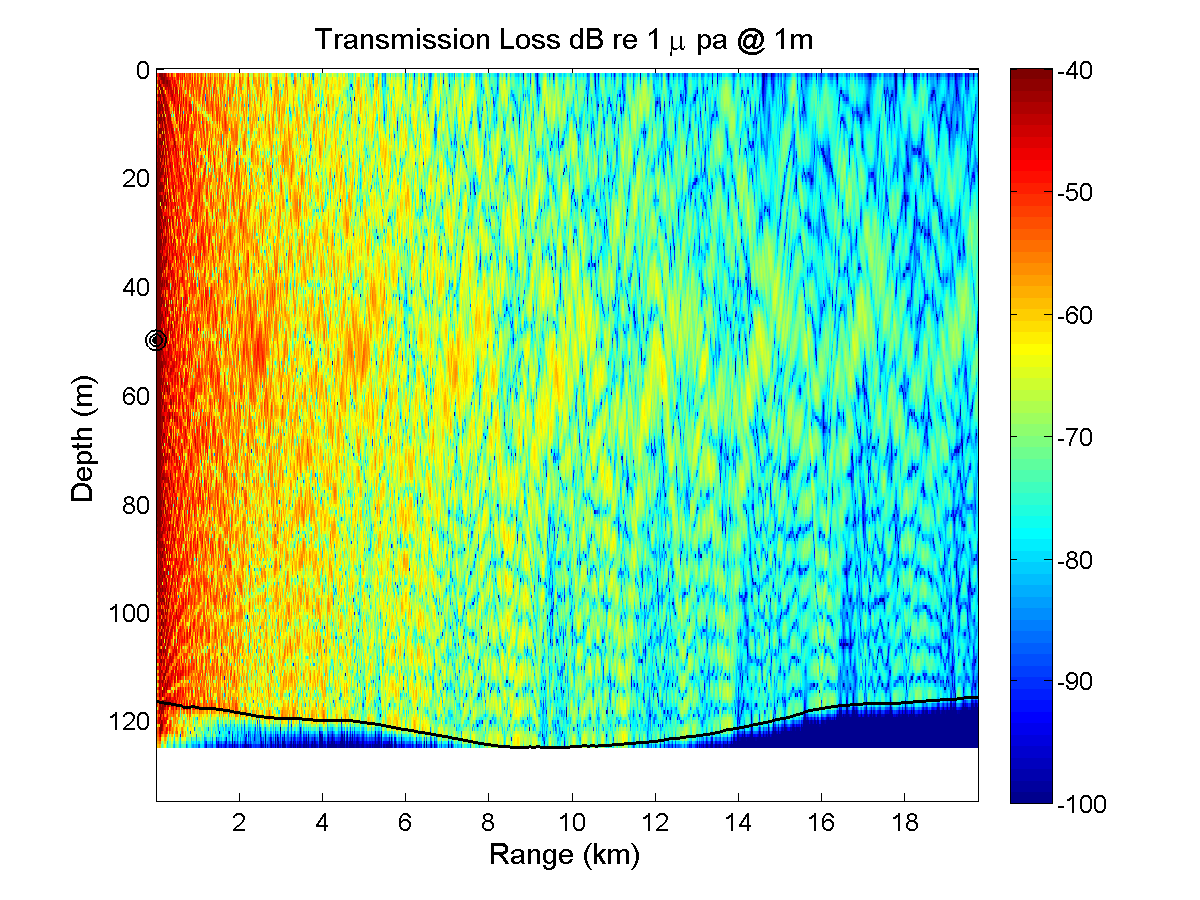
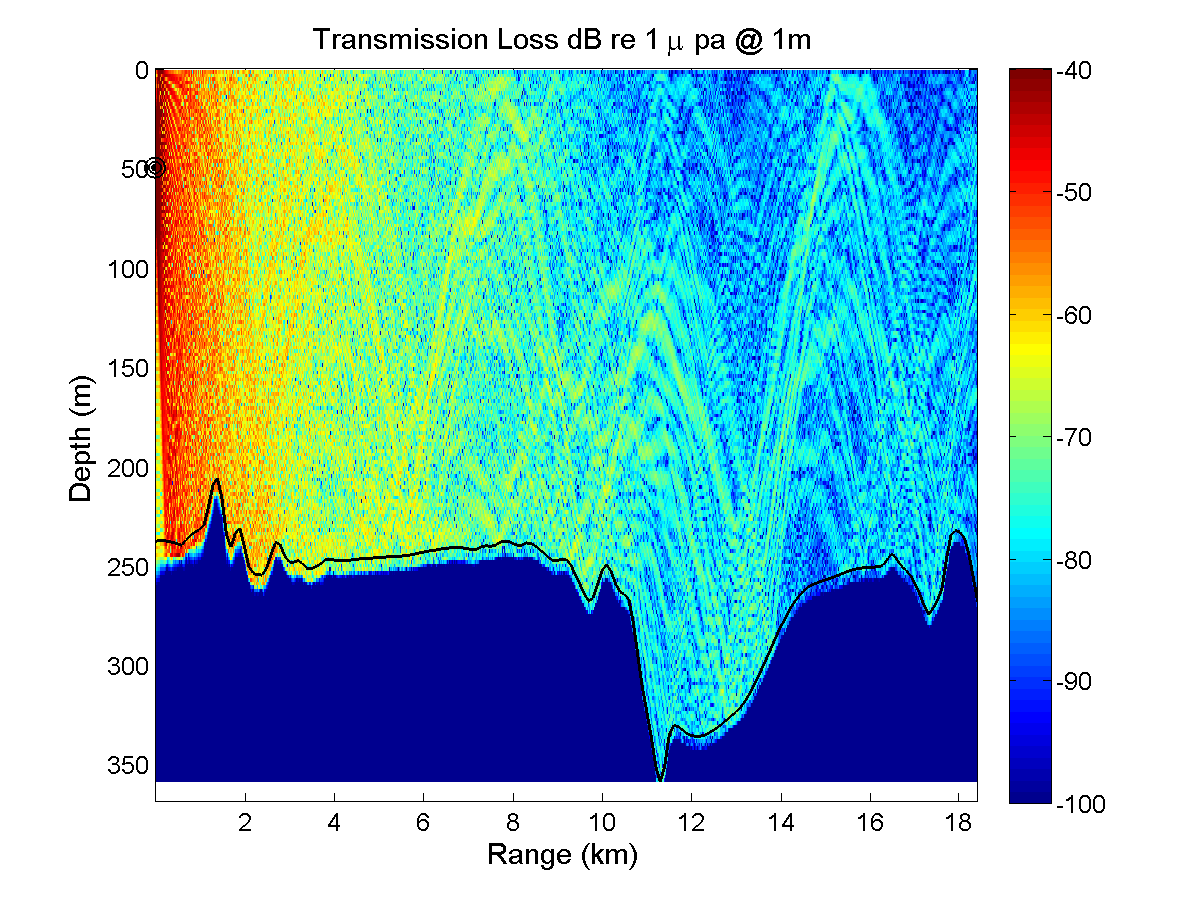
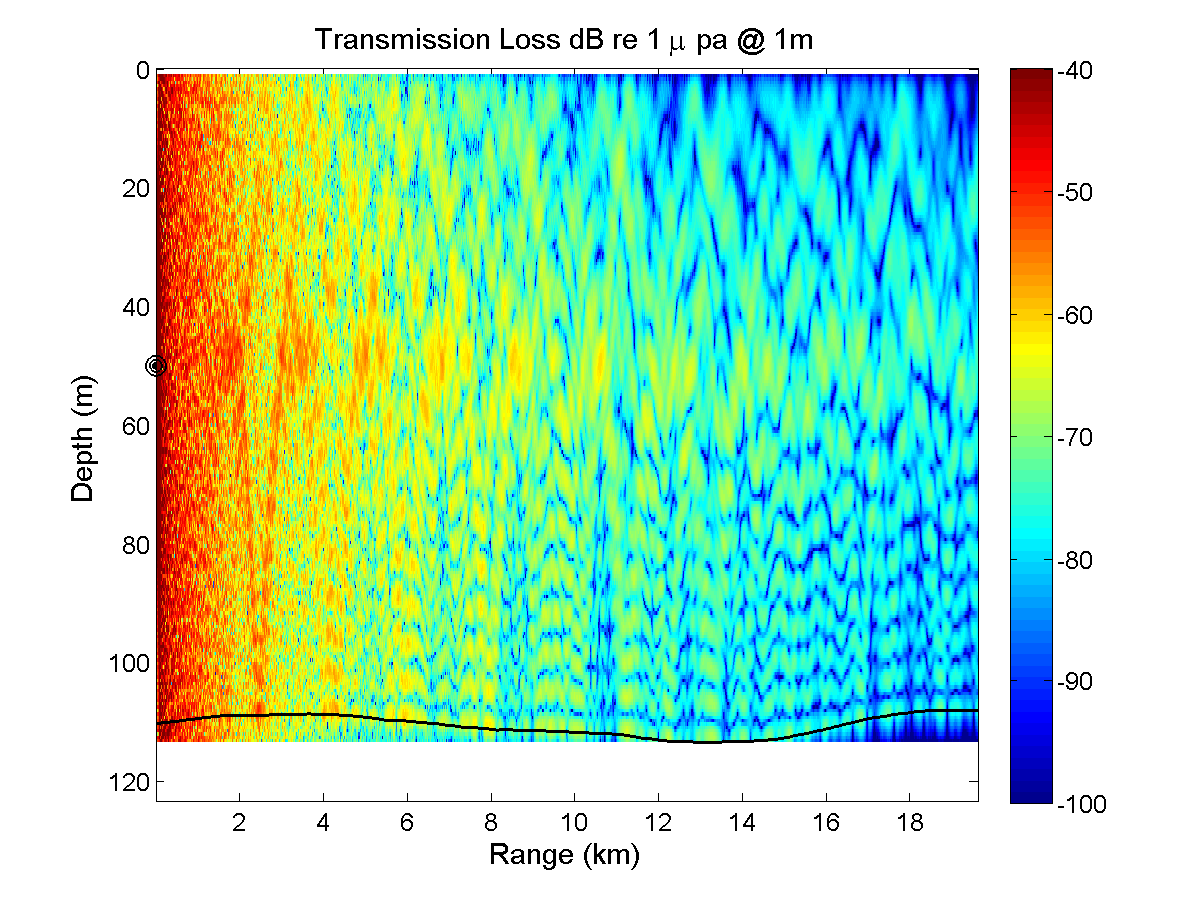
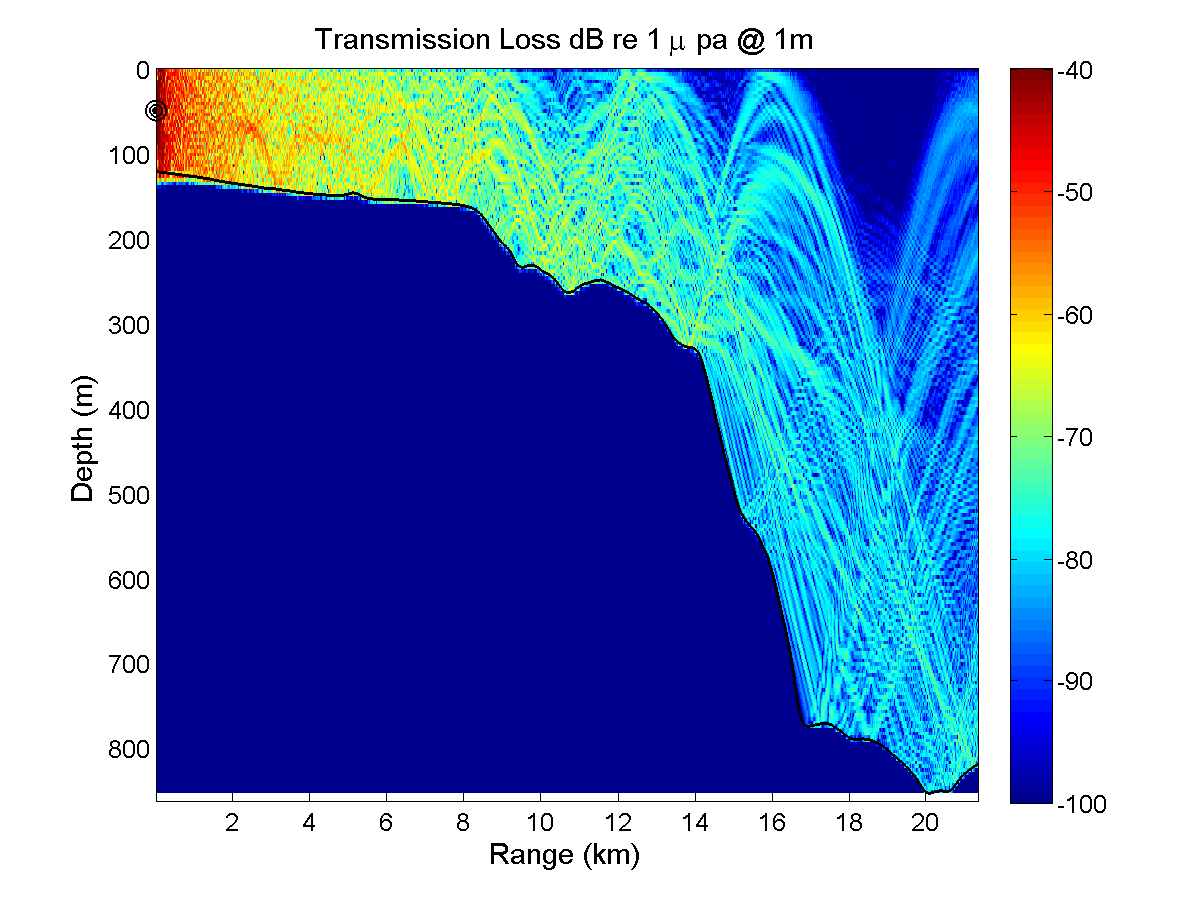
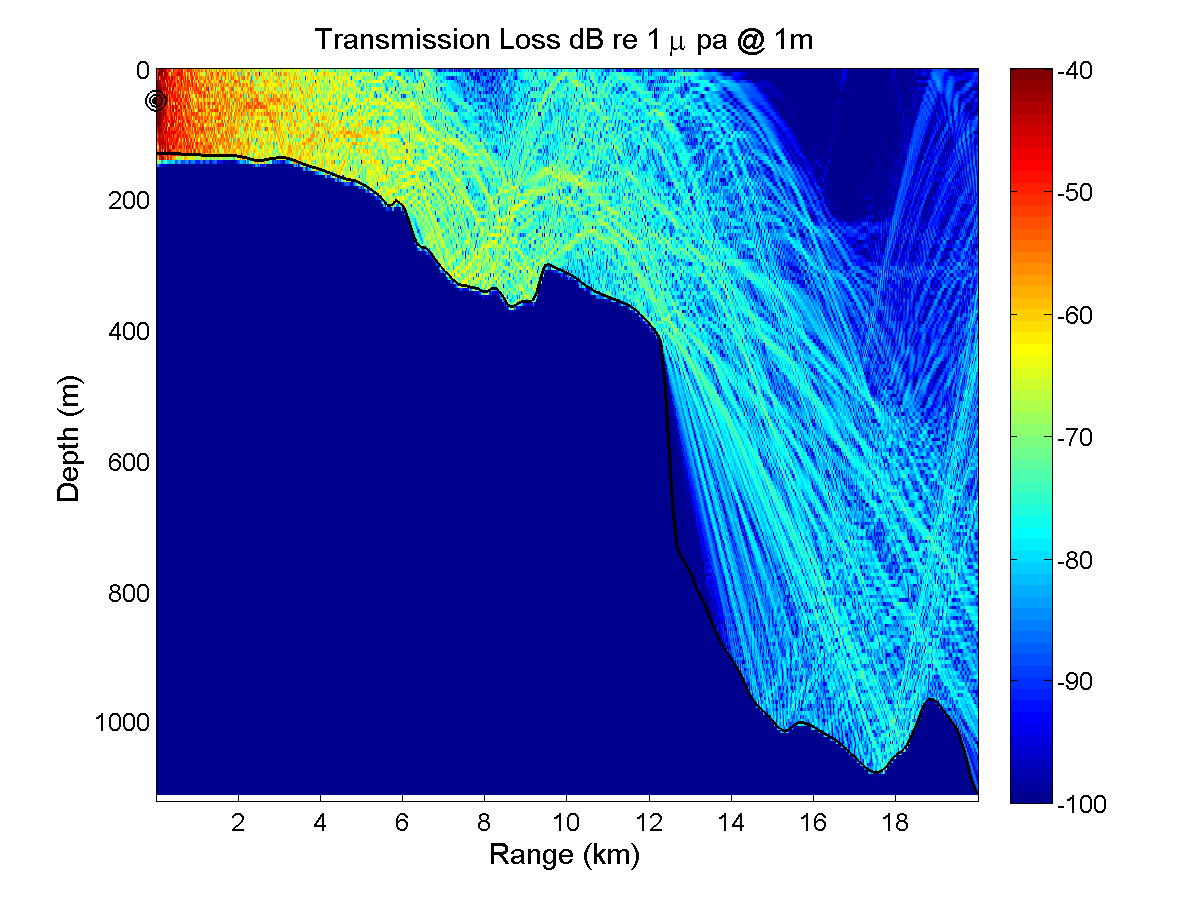
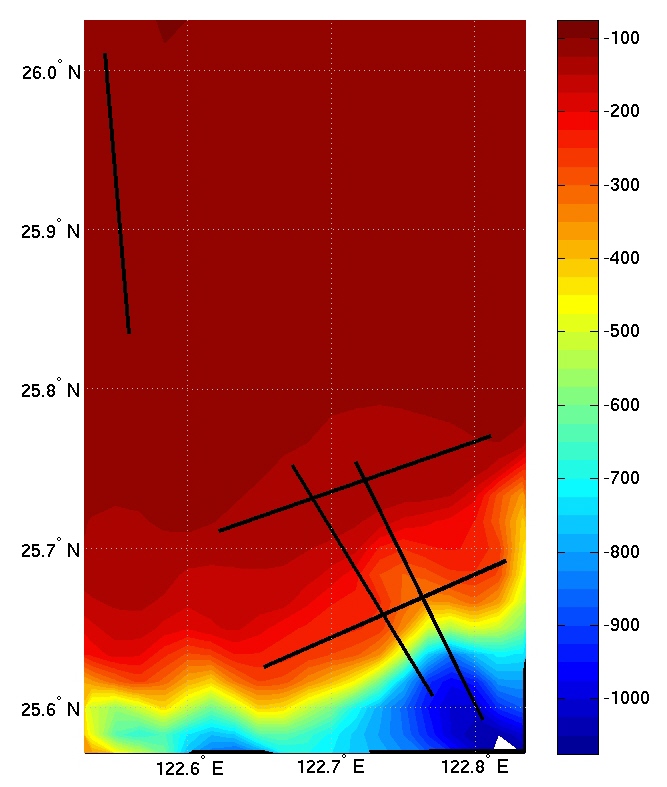
Five 20 km long acoustic propagation paths were identified during a planning meeting at MIT in order to explore the acoustic propagation properties in the intensive QPE study area. Those five paths generally represent typical transmission paths for exploring effects of ocean variability in this intensive region. The frequencies chosen were 300, 600, and 900 Hz; which are in the range of OMAS sources. The source depth was set at 50m below the sea surface. Acoustic simulations were run in both along-section directions for each frequency and for two ocean conditions, one with a significant southward transport (2.5 Sv) in the Taiwan Straits and the other with a northward transport of 1.0 Sv. Importantly, these ocean simulations do not contain tidal effects and are started from summer climatological fields. The simulated ocean variability is thus smaller than the real one, implying that the acoustic variability is likely also underestimated. Acoustic simulations are performed with the Coupled SACLANTCEN normal mode propagation loss model (C-SNAP). It is a range-dependent one-way coupled modes model with impedance matching to account for energy conservation.
Snapshots of physical properties (temperature, salinity, velocity) from the simulation with a fixed 1.0 Sv northward transport can be found here, and the snapshots from the simulation with a free 2.5 Sv southward transport can be found here.

|
Examples from different acoustic propagation paths Click on section name for complete set of plots (900Hz - 2.5Sv Transport) |
|||||
| Sep. 07, 2008 | Along Shelf1 | Along Shelf2 | Across Shelf1 | Across Shelf2 | Along Canyon | |

|

|

|

|

|
||
For this initial study the sea bed bottom is chosen as a range independent geoacoustic model. Our purpose is to show variability of the acoustic transmission loss estimations through the effect of water column fluctuations. The uncertainty of bathymetry and seabed bottom properties certainly affects the ability of acoustic transmission loss prediction. The seabed bottom properties used in our acoustic propagation model are listed here:
| Sea Bed Parameters | |||
| Cb | Rho | Attenuation | |
| 5m Muddy-Sand Sediment layer | 1549 m/s | 1.488 g/cm3 | 0.126 db/lambda |
| Hard bottom of Half-space below | 2000 m/s | 2.05 g/cm3 | 0.1 db/lambda |
Return to the MSEAS QPE real-time web page