Sea Exercises
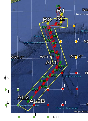
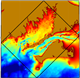
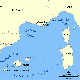
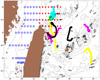
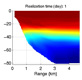
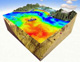
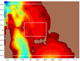
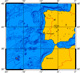
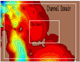
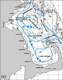
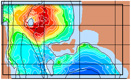
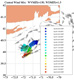
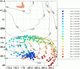
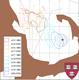
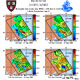
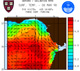
To test and validate new theories, methodologies and systems, it is essential to work with real ocean data. Data motivate discoveries and foster new fundamental ideas. Such sea experiments are our group’s laboratory. We have participated in 47 real-time experiments, with multiple institutions, at both the national and international levels, and involving a plethora of sensors and platforms. Depending on the exercise’s specific goals, we forecast ocean fields and uncertainties, optimize sampling operations, assimilate data and/or describe the multi-scale dynamics.
Below is a list of exercises in which we have participated.